The online food delivery industry has experienced massive growth over the last decade, driven by changing consumer habits, mobile technology, and urban lifestyles. Platforms like Uber Eats, DoorDash, and Deliveroo have reshaped how people order food but Just Eat remains one of the most established and profitable players, especially in Europe.
What Is Just Eat?
Just Eat is an online food ordering and delivery marketplace that connects customers with local restaurants through its mobile app and website. Founded in Denmark in 2001, the company expanded rapidly across Europe and later merged with Takeaway.com to form Just Eat Takeaway.com.
Today, Just Eat operates in multiple countries, serving millions of customers and partnering with a vast network of restaurants. Its core offering is a digital platform for food discovery, ordering, payment, and delivery, designed to simplify the entire food ordering experience.
How Just Eat Works
How Just Eat Works for Customers
Customers use Just Eat to search for nearby restaurants based on cuisine type, ratings, delivery time, and price. The platform allows users to place orders seamlessly, pay online, and track their food in real time.
Just Eat offers both delivery and pickup options, giving customers flexibility. Frequent promotions, discounts, and personalized recommendations help improve customer satisfaction and encourage repeat orders.
How Just Eat Works for Restaurants
Restaurants join Just Eat by listing their menus, setting prices, and choosing whether to manage delivery themselves or use Just Eat’s courier services. Orders are transmitted digitally, reducing manual errors and operational friction.
In addition to order management, Just Eat provides marketing exposure, customer analytics, and demand generation, helping restaurants increase sales without investing heavily in their own digital infrastructure.
Just Eat Business Model Explained
Just Eat operates a two-sided marketplace business model, connecting customers on one side and restaurants on the other. The platform acts as an intermediary, facilitating transactions while collecting fees for its services.
Originally built as an asset-light marketplace, Just Eat allowed restaurants to handle their own deliveries. Over time, the company adopted a hybrid model, offering delivery services in selected markets to improve customer experience and increase revenue per order.
This flexible approach allows Just Eat to adapt to local market conditions while maintaining scalability.
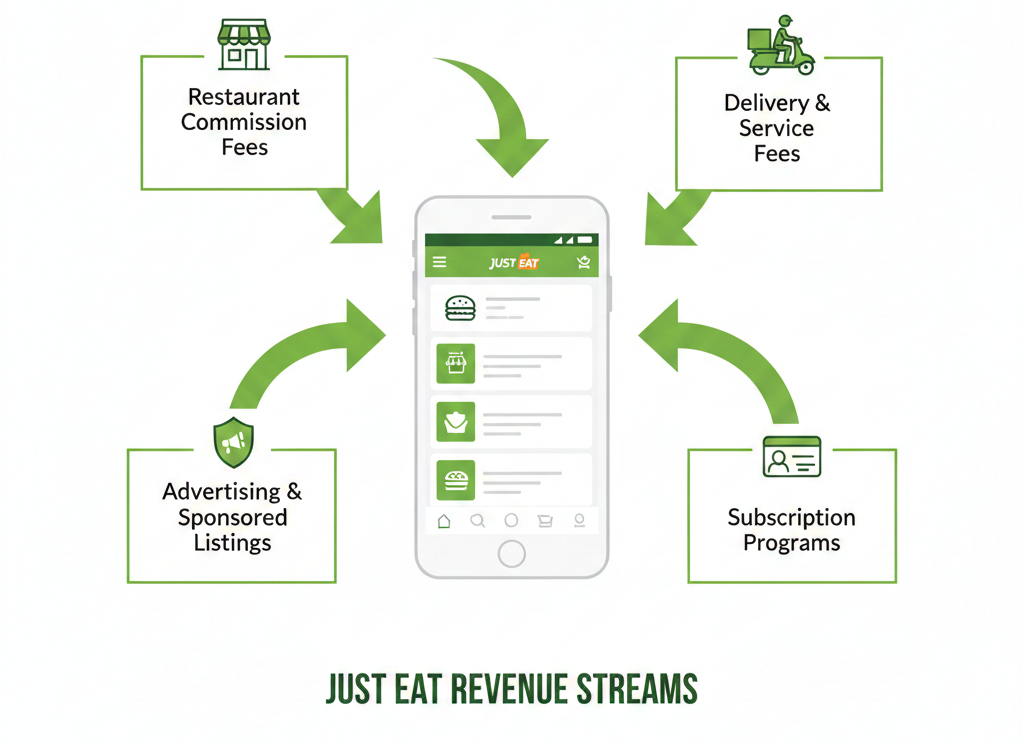
How Just Eat Makes Money
Commission Fees from Restaurants
The largest revenue source in the Just Eat business model is commission-based fees charged to restaurants. Restaurants pay a percentage of each order placed through the platform.
Marketplace-only restaurants pay lower commissions, while those using Just Eat’s delivery services pay higher fees. This pricing structure aligns costs with the level of service provided.
Delivery Fees and Service Charges
Just Eat also earns revenue through customer-paid delivery fees, especially in markets where it operates its own courier network. Service fees may be added to cover platform maintenance and operational costs.
These fees help offset high logistics expenses and improve unit economics.
Advertising and Sponsored Restaurant Listings
Advertising is a fast-growing and high-margin revenue stream for Just Eat. Restaurants can pay for sponsored listings, featured placements, and promotional campaigns to increase visibility on the platform.
Since these ads target users who are already searching for food, they deliver strong conversion rates for restaurants and attractive margins for Just Eat.
Subscription and Loyalty Programs
In some markets, Just Eat offers subscription-based programs that provide benefits such as reduced delivery fees or exclusive discounts. These programs increase customer retention, order frequency, and predictable recurring revenue.
Just Eat Value Proposition
Value Proposition for Customers
For customers, Just Eat delivers convenience, choice, and reliability. Users gain access to a wide selection of restaurants, easy ordering, secure payments, and flexible delivery options—all in one app.
Deals, discounts, and loyalty rewards further enhance customer value and encourage long-term engagement.
Value Proposition for Restaurants
For restaurants, Just Eat provides access to a large, ready-to-order customer base without the need to build their own online ordering system. The platform helps increase order volume, improve visibility, and scale digital sales efficiently.
Delivery support and marketing tools make Just Eat especially valuable for small and medium-sized restaurants.
Key Resources and Technology Behind Just Eat
Technology is at the core of Just Eat’s operations. The company’s mobile apps and website power restaurant discovery, order placement, and payments. Advanced data analytics and recommendation systems optimize pricing, delivery times, and customer engagement.
In delivery-enabled markets, logistics infrastructure and courier management systems play a critical role in ensuring fast and reliable service.
Customer Acquisition and Marketing Strategy
Just Eat uses a combination of digital marketing, app-based promotions, and referral programs to acquire customers. First-time user discounts and targeted campaigns help drive app installs and initial orders.
Strategic partnerships and local branding efforts strengthen market presence and improve customer trust in competitive regions.
Just Eat Competitive Advantage
Just Eat’s competitive advantage lies in its strong brand recognition across Europe, extensive restaurant network, and flexible hybrid business model. Unlike delivery-only platforms, Just Eat can operate profitably in both marketplace-driven and delivery-driven environments.
Its long-standing relationships with local restaurants create high switching costs and defensibility.
Competitors and Market Position
Just Eat competes with major food delivery platforms such as Uber Eats, DoorDash, and Deliveroo. While global competitors focus heavily on logistics and rapid expansion, Just Eat differentiates itself through local market dominance and a balanced approach to delivery and marketplace services.
This positioning allows Just Eat to maintain relevance and scale in mature markets.
Costs, Risks, and Challenges
Delivery and logistics costs remain a major challenge, particularly in courier-heavy markets. Rising competition increases customer acquisition costs and pressures commission rates.
Additionally, regulatory and labor issues related to gig economy workers pose ongoing operational and legal risks.
Future Growth Opportunities for Just Eat
Future growth opportunities include grocery and convenience delivery, deeper penetration of subscription programs, and continued optimization of delivery efficiency through technology.
Expanding into underserved regions while strengthening profitability in existing markets will be critical to long-term success.
Conclusion: Is the Just Eat Business Model Sustainable?
The Just Eat business model succeeds by creating value for both customers and restaurants while monetizing through commissions, delivery fees, and advertising. Its hybrid approach offers flexibility, scalability, and resilience in a highly competitive market.
Despite challenges related to costs and regulation, Just Eat’s strong brand, large restaurant network, and diversified revenue streams position it well for sustainable growth in the evolving online food delivery industry.
Discover more from Business Model Hub
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.