Short answer: DeepSeek’s business model is built around open-source AI models combined with enterprise-level usage, API access, and strategic ecosystem adoption, allowing it to grow influence first and monetise selectively.
To really understand DeepSeek’s business model, we need to look at why it focuses on open models, how it attracts developers, and where money actually comes in.
What Is DeepSeek?
DeepSeek emerged from China as an AI research-driven company that took a fundamentally different approach than most of its competitors. While companies like OpenAI and Anthropic built closed ecosystems with paywalled access, DeepSeek decided to release powerful language models with open or semi-open access.
The company gained global attention when its models—particularly DeepSeek-V3 and DeepSeek-R1—demonstrated performance rivaling GPT-4 and Claude at a fraction of the reported training cost. This wasn’t just impressive from a technical standpoint; it represented a strategic business decision that challenged conventional wisdom about how AI companies should operate.
What makes DeepSeek different: Unlike typical closed AI companies that treat their models as proprietary secrets, DeepSeek positions itself as infrastructure. It’s not just selling AI—it’s building foundational layers that other companies, developers, and researchers can build upon.
DeepSeek’s Core Value Proposition
DeepSeek offers several compelling advantages that attract different types of users:
High-performance large language models that compete with the best closed-source alternatives, particularly strong in reasoning, mathematics, and coding tasks.
Open or semi-open access that allows developers to experiment, modify, and deploy without restrictive licensing or usage limitations that hamper innovation.
Cost-efficient alternatives to Western AI models, both in terms of training efficiency and inference costs, making advanced AI accessible to organizations with limited budgets.
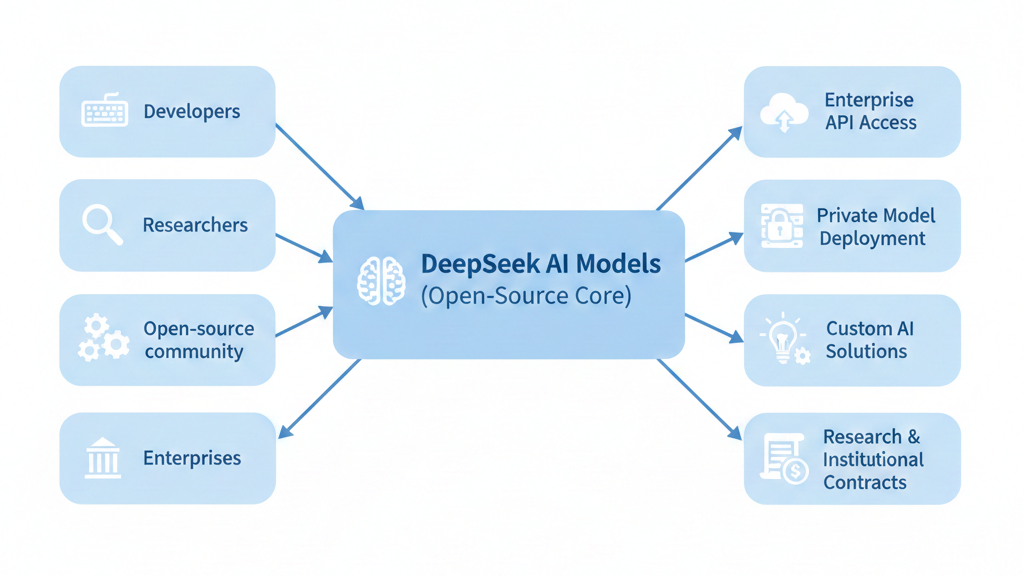
Who benefits most from DeepSeek:
- Developers who want to experiment without credit card requirements or usage limits
- Startups building AI products that need powerful models without enterprise pricing
- Enterprises looking for alternatives they can host internally or customize extensively
- Research institutions requiring transparent, accessible models for academic work
DeepSeek’s Target Customers
DeepSeek serves distinct customer segments, each with different needs:
Individual developers & researchers: Students, hobbyists, and independent developers exploring AI capabilities or building personal projects.
AI startups building on LLMs: Early-stage companies that need powerful models but can’t justify OpenAI or Anthropic’s enterprise costs.
Enterprises integrating AI internally: Organizations wanting to deploy AI for internal use cases like customer service, data analysis, or automation.
Institutions & organisations needing custom models: Universities, government agencies, and large corporations requiring models they can modify, audit, or host on their own infrastructure.
DeepSeek Business Model Explained (Simple Breakdown)
a) Open-Source-Led Growth Model
DeepSeek’s primary strategy is giving away significant value upfront to build a massive user base and ecosystem:
Free access to models creates rapid adoption among developers who would never pay for closed alternatives. This generates word-of-mouth, community trust, and experimentation that money can’t buy.
Community trust develops as researchers can inspect model behavior, developers can test without barriers, and organizations can evaluate without sales calls.
Ecosystem expansion before monetisation means DeepSeek prioritizes becoming indispensable before aggressively extracting value—a patient capital approach that builds long-term defensibility.
b) Platform & Infrastructure Play
DeepSeek positions itself as foundational infrastructure rather than just another AI product:
Models as foundational layers that other companies build upon, similar to how Linux became infrastructure for the internet despite being free.
Default intelligence for some use cases: For developers in certain regions or industries, DeepSeek is becoming the obvious choice—not through marketing, but through availability and performance.
How DeepSeek Makes Money (Revenue Streams)
While DeepSeek’s open approach might seem anti-commercial, the company has several actual and potential revenue streams:
Enterprise API access: While basic usage might be free or low-cost, high-volume enterprise customers pay for API access with guaranteed uptime, speed, and support. This is similar to how MongoDB or Redis offer free open-source versions but charge for managed services.
Custom model deployment for businesses: Organizations often want DeepSeek’s technology but need it customized for their specific use case, industry, or language. DeepSeek can charge substantial fees for this specialized work.
Private hosting & infrastructure services: Many enterprises prefer AI models running on their own servers for security, compliance, or data privacy reasons. DeepSeek can provide deployment support, infrastructure consulting, and ongoing maintenance.
Research partnerships & institutional contracts: Universities, government agencies, and large research organizations may contract with DeepSeek for specialized model development or collaborative research initiatives.
Future monetisation potential: As the ecosystem matures, DeepSeek could introduce premium developer tools, fine-tuning platforms, licensing for specific commercial applications, or marketplace services.
Important note: DeepSeek’s monetisation is selective, not aggressive. The company isn’t trying to squeeze revenue from every user—it’s building an installed base that will support premium services later.
Cost Structure: Where DeepSeek Spends Money
Understanding DeepSeek’s costs helps explain why its business model is viable:
Model training and compute: The largest expense—training frontier models requires enormous computational resources, though DeepSeek claims efficiency advantages over competitors.
Research talent and engineers: Top AI researchers and machine learning engineers command premium salaries, particularly in competitive markets.
Infrastructure and optimisation: Ongoing costs for inference servers, model optimization, and platform maintenance as usage scales.
Security and deployment support: Ensuring models are safe, reliable, and properly deployed for enterprise customers requires dedicated teams.
Despite these costs, DeepSeek’s reported training efficiency gives it structural cost advantages that enable its open approach.
Why DeepSeek Chooses Open Models (Strategic Logic)
DeepSeek’s open-source strategy isn’t altruism—it’s calculated business strategy:
Faster adoption vs closed competitors: Developers try DeepSeek because there’s no friction. No credit card, no approval process, no sales call. This creates exponential growth in users.
Lower distribution friction: Traditional enterprise software requires expensive sales teams. DeepSeek’s models sell themselves through developer adoption that pulls in enterprise buyers.
Community-driven innovation: When thousands of developers experiment with your models, they discover use cases, identify problems, and build applications you could never imagine internally.
Long-term platform power instead of short-term revenue: DeepSeek is playing for market position, not quarterly earnings. Once your models become infrastructure that others depend on, you have leverage that closed systems can’t replicate.
This mirrors successful strategies from Linux, Android, and Kubernetes give away the core, monetize the ecosystem.
DeepSeek vs OpenAI vs Anthropic (Business Model Comparison)
| Dimension | DeepSeek | OpenAI | Anthropic |
|---|---|---|---|
| Openness | Open/semi-open models | Closed, API-only | Closed, API-only |
| Monetisation timing | Later, ecosystem-first | Immediate, aggressive | Moderate, enterprise-focused |
| Target customers | Developers → Enterprises | Consumers + Enterprises | Enterprises primarily |
| Strategic priorities | Market share, adoption | Revenue growth, scale | Safety, enterprise trust |
Key insight: OpenAI and Anthropic optimize for revenue today. DeepSeek optimizes for market position tomorrow. Both can be correct depending on their capital structures and strategic goals.
Growth Strategy: How DeepSeek Scales
DeepSeek’s growth doesn’t rely on traditional marketing:
Developer-first adoption: Free, powerful models create thousands of developers who become familiar with DeepSeek’s ecosystem. When they join companies or start businesses, they bring DeepSeek with them.
Word-of-mouth within AI community: Impressive benchmarks and cost efficiency create organic discussion in forums, social media, and technical communities—more credible than advertising.
Research credibility as marketing: Publishing papers, releasing benchmarks, and contributing to AI research builds reputation that translates into trust and adoption.
Strategic partnerships: Collaborating with cloud providers, AI platforms, and enterprise software companies creates distribution channels and legitimacy.
This bottoms-up, product-led growth strategy scales efficiently because satisfied users become advocates.
Risks & Challenges in DeepSeek’s Business Model
No business model is without vulnerabilities:
High compute costs: Training and running frontier models is expensive. If DeepSeek can’t maintain cost efficiency or secure compute access, the economics break down.
Monetisation pressure: Eventually, investors or stakeholders will want returns. Transitioning from free to paid without alienating the community is notoriously difficult.
Regulatory scrutiny: As a Chinese AI company operating globally, DeepSeek faces potential regulatory restrictions, data localization requirements, or geopolitical pressures.
Competition from closed-source giants: OpenAI, Anthropic, and Google have more capital and can subsidize prices to maintain market share. They could also copy DeepSeek’s open approach if threatened.
Commoditization risk: If all models become open and similar in performance, differentiation disappears and margins compress.
What Founders Can Learn from DeepSeek
DeepSeek’s strategy offers lessons beyond AI:
When to delay monetisation: If you’re building infrastructure or platforms, early monetization can limit growth. Sometimes giving away significant value creates more long-term leverage than extracting revenue immediately.
How open ecosystems create leverage: Transparency and accessibility build trust and adoption that closed systems can’t match. Once people build on your platform, switching costs protect you.
Why infrastructure businesses win long-term: Companies selling picks and shovels during a gold rush often outlast companies mining for gold. DeepSeek is building AI infrastructure, not just another chatbot.
Product-led trust as a growth strategy: Letting your product speak through free access is often more effective than sales and marketing, particularly for technical audiences.
Future of DeepSeek’s Business Model
Looking ahead, DeepSeek’s business model will likely evolve:
Shift toward enterprise dominance: As the developer community matures, enterprise contracts will become the primary revenue driver—similar to how Red Hat monetized Linux.
More private deployments: Organizations increasingly want AI running on their own infrastructure. DeepSeek is well-positioned to provide deployment services, consulting, and support.
AI infrastructure positioning: DeepSeek may evolve beyond models to offer complete AI infrastructure stacks—training platforms, fine-tuning tools, deployment solutions—becoming the “AWS of AI.”
Long-term platform economics: As ecosystem lock-in strengthens, DeepSeek can introduce premium services, marketplace fees, or platform charges that generate recurring revenue from a captive base.
Final Take: Is DeepSeek’s Business Model Sustainable?
Verdict: Yes, but with important caveats.
DeepSeek’s business model is sustainable if the company can successfully navigate from growth to monetization without losing its community. The infrastructure-first, open-source-led approach has proven successful in other technology categories, and AI is following similar patterns.
This model works best for:
- Companies with patient capital that can invest in long-term market position
- Organizations with structural cost advantages that enable giving away value
- Platforms where network effects and ecosystem lock-in create defensibility
- Markets where trust and transparency provide competitive advantages
Why DeepSeek is playing a long game:
DeepSeek isn’t optimizing for next quarter’s revenue. It’s building market position that will generate sustainable returns for decades. By becoming infrastructure that developers and enterprises depend on, DeepSeek creates leverage that closed competitors cannot easily replicate.
Discover more from Business Model Hub
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.

Pingback: Anthropic Business Model Explained