South Korea’s food delivery market is one of the most sophisticated in the world, and at its center stands Baemin (Baedal Minjok), the undisputed market leader. But how exactly does Baemin make money? In this comprehensive analysis, we’ll break down Baemin’s business model, revenue streams, competitive advantages, and the strategic framework that powers this multi-billion dollar platform.
What is Baemin?
Baemin, short for Baedal Minjok (meaning “Delivery Nation” in Korean), is South Korea’s largest food delivery and lifestyle platform. Launched in 2010, Baemin has evolved from a simple restaurant listing service into a comprehensive local commerce ecosystem.
The platform serves as a digital marketplace connecting three essential groups:
- Hungry customers seeking convenient meal delivery
- Restaurants looking to expand their digital presence and sales
- Delivery partners providing the critical last-mile logistics
Today, Baemin commands over 60% market share in South Korea’s competitive food delivery landscape, processing millions of orders daily and generating billions in gross merchandise value (GMV).
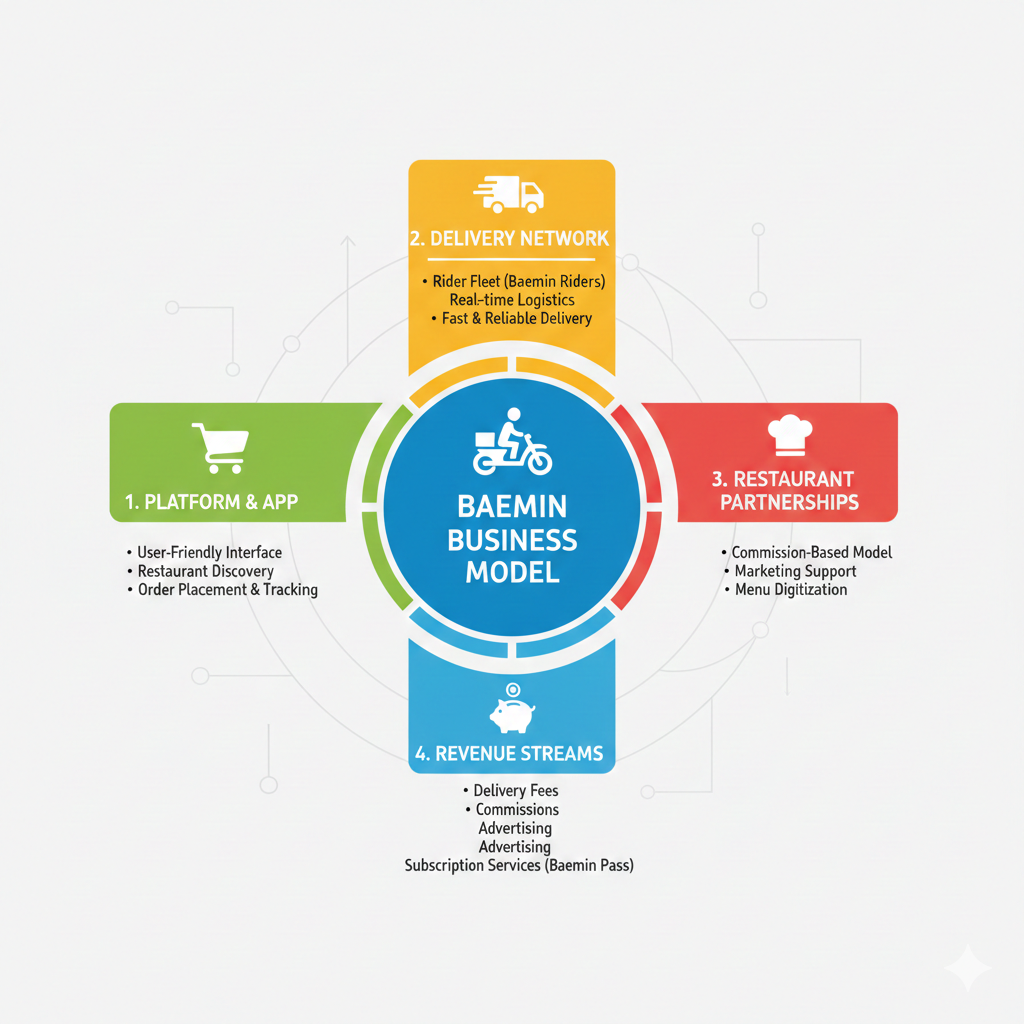
How Baemin Makes Money: Revenue Streams Explained
Baemin’s financial success stems from a diversified revenue model that monetizes multiple aspects of its platform. Unlike traditional businesses that rely on a single income source, Baemin generates revenue through five primary streams:
Restaurant Commission Fees
The backbone of Baemin’s revenue comes from commissions charged to restaurants for each order placed through the platform. Commission rates typically range from 6% to 12% of the order value, varying based on:
- Service tier selected by the restaurant
- Marketing visibility packages
- Order volume commitments
- Logistics support requirements
This commission-based model aligns Baemin’s success with restaurant sales growth, creating a mutually beneficial relationship.
Customer Delivery Fees
Customers pay delivery charges that vary dynamically based on several factors:
- Distance from restaurant to delivery location
- Time of day and demand levels
- Weather conditions
- Restaurant partnership agreements
Some restaurants offer free delivery promotions, either absorbing the cost themselves or sharing it with Baemin as part of marketing campaigns.
Advertising and Sponsored Placements
Baemin’s platform generates significant advertising revenue from restaurants competing for customer attention. Restaurants pay premium fees for:
- Sponsored listings appearing at the top of search results
- Category page banners showcasing special promotions
- Premium placement in curated collections and recommendations
- Push notification campaigns targeting specific customer segments
This advertising model mirrors successful marketplace platforms like Amazon and eBay, where visibility directly correlates with sales.
Subscription and SaaS Services
Baemin offers premium subscription services for restaurants, including:
- Advanced analytics and customer insight dashboards
- Professional order management systems
- Marketing automation tools
- Inventory management integration
- Customer relationship management (CRM) features
These software-as-a-service (SaaS) offerings create recurring revenue while deepening Baemin’s integration into restaurant operations.
Logistics and Delivery Services
Through its proprietary delivery network, Baemin Riders, the platform offers end-to-end logistics services. Restaurants can outsource their entire delivery operations to Baemin, paying fees based on:
- Delivery distance and complexity
- Peak vs. off-peak timing
- Volume commitments
- Service level agreements
This vertical integration gives Baemin greater control over the customer experience while creating an additional revenue stream.
Understanding Baemin’s Value Proposition
Successful platforms must deliver compelling value to all participants. Here’s what makes Baemin indispensable to each stakeholder:
For Customers
Convenience at Scale: Baemin’s intuitive mobile app makes ordering food effortless, with features like saved addresses, payment methods, and favorite restaurants accessible in just a few taps.
Unmatched Selection: With hundreds of thousands of restaurants on the platform, customers enjoy incredible variety spanning from local favorites to major chains, Korean cuisine to international options.
Reliable Delivery: Real-time order tracking, accurate delivery estimates, and a professional delivery network ensure customers know exactly when their food will arrive.
Value Through Promotions: Regular discounts, coupon codes, and loyalty programs make Baemin an affordable option for frequent users.
Trust and Reliability: As South Korea’s most recognized delivery brand, Baemin benefits from strong brand trust and consistent service quality.
For Restaurants
Customer Access: Baemin provides instant access to millions of active users, dramatically expanding a restaurant’s potential customer base beyond walk-in traffic.
Incremental Revenue: Many restaurants report that delivery orders through Baemin represent net-new revenue rather than cannibalization of existing dine-in sales.
Marketing Infrastructure: Small restaurants gain access to sophisticated marketing tools typically available only to large chains, including targeted promotions and customer analytics.
Operational Support: Baemin’s logistics network eliminates the need for restaurants to manage their own delivery staff, reducing overhead and complexity.
Data-Driven Insights: Detailed analytics help restaurants understand customer preferences, optimize menus, adjust pricing, and identify peak demand periods.
For Delivery Partners
Flexible Income: Delivery riders can work on their own schedules, choosing when and how much to work based on personal needs.
High Demand Density: Baemin’s market dominance ensures consistent order flow, particularly in urban areas, maximizing earning potential per hour.
Streamlined Operations: The rider app efficiently manages order assignments, navigation, and earnings tracking, simplifying the work experience.
Baemin Business Model Canvas: A Strategic Framework
To fully understand how Baemin operates, let’s map its business model using the Business Model Canvas framework, a strategic management tool that visualizes the key components of a business.
Key Partners
Baemin’s ecosystem depends on strategic partnerships with multiple stakeholders:
- Restaurant partners ranging from independent eateries to major franchise chains
- Delivery riders operating as independent contractors or through partner agencies
- Payment processors enabling seamless financial transactions
- Cloud kitchen operators creating delivery-optimized food preparation facilities
- Technology vendors providing infrastructure and development support
- Marketing agencies amplifying brand awareness
Key Activities
The core activities that make Baemin’s platform function include:
- Platform development and continuous technological improvement
- Customer acquisition through digital marketing and brand campaigns
- Restaurant onboarding and relationship management
- Delivery logistics coordination and optimization
- Quality assurance monitoring for food safety and service standards
- Data analytics for personalization and operational efficiency
- Customer support handling inquiries and resolving issues
Key Resources
Baemin’s competitive advantages are built on critical resources:
Technological Assets:
- Advanced mobile applications for customers, restaurants, and riders
- Sophisticated backend systems handling millions of transactions
- Machine learning algorithms for demand forecasting and route optimization
Data Assets:
- Comprehensive customer ordering patterns and preferences
- Restaurant performance metrics and operational data
- Delivery logistics data optimizing efficiency
Brand Assets:
- Strong brand recognition and emotional connection in South Korea
- Reputation for reliability and customer service
- Cultural relevance through localized marketing
Physical Assets:
- Logistics infrastructure and delivery fleet
- Customer service centers
- Technology development facilities
Network Assets:
- Extensive restaurant partnerships
- Large active delivery rider network
- Growing customer base with high retention rates
Value Propositions
Baemin’s value propositions have been detailed above, offering convenience and selection for customers, growth and tools for restaurants, and flexible earning for delivery partners.
Customer Relationships
Baemin maintains relationships with its users through:
- Self-service platform enabling autonomous ordering and management
- Automated support via chatbots and FAQ systems
- Personalized recommendations based on order history and preferences
- Loyalty programs rewarding frequent users
- Community engagement through social media and brand content
- Proactive communication about order status and promotions
Channels
Baemin reaches its customers through multiple channels:
- Mobile application (primary interface for all user types)
- Website for browsing and ordering
- Social media for marketing and customer engagement
- In-app notifications for timely promotions and updates
- Email marketing for retention and re-engagement
- Offline marketing including subway ads and sponsorships
Customer Segments
Baemin serves several distinct customer segments:
Consumer Segments:
- Young professionals seeking convenience
- Students on limited budgets
- Families ordering for multiple people
- Late-night workers needing food options
Business Segments:
- Independent restaurants seeking growth
- Franchise chains expanding delivery
- Cloud kitchens operating delivery-only concepts
- Corporate caterers serving businesses
Service Provider Segments:
- Full-time delivery riders
- Part-time gig workers
- Delivery fleet operators
Cost Structure
Running a food delivery platform involves substantial costs:
Variable Costs:
- Delivery rider payments and incentives (largest expense)
- Payment processing fees
- Customer acquisition costs
- Promotional discounts and subsidies
Fixed Costs:
- Technology development and maintenance
- Cloud infrastructure and servers
- Marketing and brand building
- Customer support operations
- Administrative and compliance costs
- Office facilities and corporate overhead
The food delivery industry operates on notoriously thin margins, making operational efficiency and scale absolutely critical for profitability.
Revenue Streams
As detailed earlier, Baemin generates revenue through restaurant commissions, delivery fees, advertising, subscriptions, and logistics services.
What Makes Baemin Different: Competitive Advantages
In South Korea’s intensely competitive food delivery market, Baemin has pulled ahead of rivals like Coupang Eats and Yogiyo through several distinctive advantages:
Brand Power and Cultural Resonance
Baemin isn’t just a utility app it’s a cultural phenomenon in South Korea. The company invests heavily in:
Creative Marketing: Baemin’s advertising campaigns are known for humor, wit, and cultural relevance that resonates deeply with Korean consumers.
Distinctive Design: The app’s playful interface and unique visual identity make it memorable and enjoyable to use.
Emotional Connection: Through consistent branding and customer engagement, Baemin has built genuine affection among users, transcending transactional relationships.
Ecosystem Approach
While competitors focus primarily on delivery, Baemin has built a comprehensive ecosystem:
End-to-End Logistics: Owning the delivery infrastructure ensures quality control and customer experience consistency.
Restaurant Technology: SaaS tools integrate Baemin deeply into restaurant operations, creating switching costs.
Advertising Platform: A sophisticated ad network creates additional revenue while helping restaurants grow.
Data Intelligence: Advanced analytics benefit all stakeholders, from optimizing delivery routes to personalizing customer recommendations.
Market Dominance and Network Effects
Baemin’s market leadership creates powerful network effects:
For Customers: More restaurants mean better selection, driving more customer signups.
For Restaurants: More customers mean higher sales potential, attracting more restaurants.
For Riders: High order density improves earnings efficiency, attracting more delivery partners.
This virtuous cycle makes Baemin increasingly difficult to displace as the platform grows.
Growth Strategy: Expanding Beyond Food Delivery
Baemin continuously evolves beyond its core food delivery business through strategic initiatives:
Vertical Expansion
Grocery and Essentials: Baemin has expanded into quick commerce, delivering groceries, convenience items, and household essentials within minutes.
Alcohol Delivery: Partnerships with liquor stores enable responsible alcohol delivery services.
Prepared Meals and Meal Kits: Pre-packaged meal solutions target health-conscious consumers.
Technology Enhancement
AI-Powered Personalization: Machine learning algorithms improve restaurant recommendations and order predictions.
Route Optimization: Advanced algorithms reduce delivery times and costs.
Voice Ordering: Integration with smart home devices enables hands-free ordering.
Restaurant Enablement
Cloud Kitchen Support: Baemin helps restaurants launch delivery-only concepts with lower overhead.
Financial Services: Lending and payment solutions help restaurants manage cash flow.
Supply Chain Integration: Connecting restaurants with suppliers for better procurement.
Customer Retention
Subscription Programs: Premium memberships offering unlimited free delivery and exclusive perks.
Gamification: Loyalty points, challenges, and rewards increase engagement.
Social Features: Enabling group ordering and sharing favorite restaurants.
Challenges and Risks in Baemin’s Business Model
Despite its success, Baemin faces significant challenges common to food delivery platforms:
Rising Delivery Costs
Labor costs continue increasing as delivery riders demand better compensation, benefits, and working conditions. Regulatory pressures around gig worker classification could significantly impact Baemin’s cost structure.
Restaurant Relations
Many restaurant owners express frustration with commission rates, feeling trapped between needing Baemin’s customer access and protecting their margins. This tension could drive regulatory intervention or push restaurants toward alternative solutions.
Intense Competition
Well-funded competitors like Coupang Eats (backed by SoftBank) and international players continually challenge Baemin’s market position, requiring ongoing investment in marketing and promotions.
Margin Pressure
The fundamental economics of food delivery make profitability challenging. High logistics costs, competitive discounting, and customer acquisition expenses squeeze margins, requiring massive scale to achieve sustainable profits.
Regulatory Uncertainty
Government regulations around data privacy, platform monopolies, worker classification, and commission caps could significantly impact Baemin’s business model.
Key Takeaways: Why Baemin’s Business Model Works
Baemin’s success stems from several strategic decisions:
Platform Control: By owning logistics rather than purely aggregating, Baemin controls the entire customer experience and captures more value.
Multi-Sided Revenue: Diversified income streams reduce dependence on any single revenue source, creating business model resilience.
Brand Investment: Heavy marketing and design investment create emotional loyalty beyond price competition.
Restaurant Integration: Deep SaaS integration makes Baemin essential to restaurant operations, not just a marketing channel.
Data Leverage: Sophisticated analytics optimize operations while creating new revenue opportunities through insights and advertising.
Network Effects: Market leadership creates self-reinforcing advantages that compound over time.
The Future of Baemin’s Business Model
As Baemin continues evolving, several trends will shape its future:
Profitability Focus: After years prioritizing growth, expect increasing emphasis on unit economics and sustainable profitability.
Super App Evolution: Baemin may expand into additional services like ride-sharing, tickets, or retail, becoming a broader lifestyle platform.
Technology Differentiation: AI, robotics, and automation could dramatically reduce delivery costs while improving service quality.
Geographic Expansion: While dominant in South Korea, international expansion remains an opportunity for growth.
Sustainability Initiatives: Environmental concerns around packaging and delivery could drive new operational practices and business models.
Conclusion
Baemin’s business model represents the evolution of food delivery from simple aggregation to comprehensive infrastructure. By controlling logistics, integrating deeply with restaurants, building brand loyalty, and diversifying revenue streams, Baemin has created a defensible competitive position in one of the world’s most sophisticated food delivery markets.
For entrepreneurs, investors, and business analysts, Baemin offers valuable lessons in platform business models, marketplace dynamics, and the critical importance of controlling key value chain components rather than purely connecting buyers and sellers.
Discover more from Business Model Hub
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.