If you’ve ever ordered food online in India, chances are you’ve used Swiggy. From piping-hot biryanis to late-night pizza cravings, Swiggy has made ordering food as easy as tapping a few buttons. But have you ever wondered how Swiggy actually makes money and manages to grow in such a competitive market?
In this blog, I’ll break down Swiggy’s business model in detail, explain its revenue streams, operations, growth strategies, challenges, and future plans. By the end, you’ll understand why Swiggy is not just a food delivery app, but a full-fledged tech and logistics platform.
A Quick Introduction to Swiggy
Swiggy was founded in 2014 by Sriharsha Majety, Nandan Reddy, and Rahul Jaimini in Bangalore. The idea was simple: India needed a reliable food delivery platform where customers could order from their favorite restaurants without worrying about late deliveries or poor service.
Since its inception, Swiggy has grown rapidly. Today, it operates in 500+ cities across India, with millions of users and thousands of restaurant partners. Swiggy has also diversified into grocery delivery, cloud kitchens, and subscription services, making it a multi-service platform.
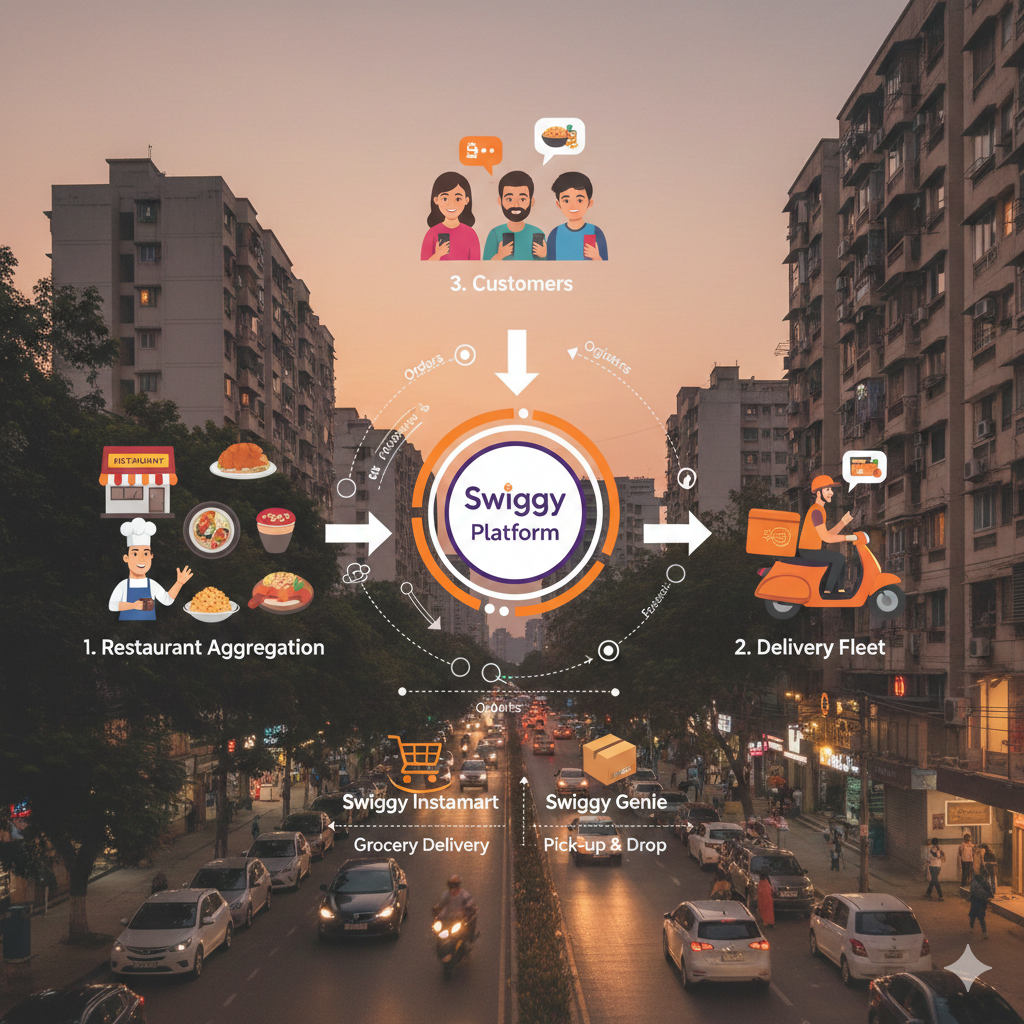
Swiggy’s Business Model Explained
At its core, Swiggy operates on a multi-sided platform model. This means it connects:
- Customers who want food delivered.
- Restaurants that want to reach more customers.
- Delivery partners who handle logistics.
The platform ensures that restaurants get more orders, customers get food conveniently, and delivery partners earn income, all while Swiggy earns money from the transactions.
Let’s break this down step by step.
Revenue Streams: How Swiggy Makes Money
Swiggy has multiple revenue streams that make its business model diverse and scalable.
1. Commission from Restaurants
The most significant revenue source for Swiggy is commission fees charged to restaurants.
- How it works: When a customer orders through Swiggy, the restaurant pays a commission for facilitating the sale.
- Example: If a meal costs ₹500 and Swiggy’s commission is 20%, Swiggy earns ₹100 from that order.
This commission varies from 15% to 25%, depending on the restaurant, location, and type of partnership. For Swiggy, this model scales revenue without owning restaurants, keeping operational costs lower.
2. Delivery Charges from Customers
Swiggy charges a delivery fee for each order, especially for smaller orders or during peak hours.
- Dynamic Pricing: Delivery charges may increase during high-demand periods, helping balance supply and demand.
- Subscription Impact: Regular users who subscribe to Swiggy’s membership plans may get free or discounted delivery.
This fee is a direct revenue source and covers part of the logistics cost.
3. Swiggy Super: Subscription Revenue
Swiggy offers Swiggy Super, a subscription service that provides:
- Free deliveries on all orders
- Discounts on select restaurants
- Exclusive deals and promotions
- Revenue benefit: Subscription revenue is predictable and recurring, unlike commission revenue, which varies with order volume.
This also increases customer loyalty, encouraging users to order more frequently.
4. Advertising Revenue
Swiggy earns money by offering promotional placements and ads to restaurants within the app.
- Restaurants pay Swiggy to appear at the top of search results, banners, or featured sections.
- This is similar to Google Ads but for food, and it can significantly boost restaurant orders.
Advertising revenue is high-margin because it doesn’t involve delivery or operational costs.
5. Swiggy Genie and Hyperlocal Services
Swiggy has diversified into hyperlocal delivery services through Swiggy Genie:
- Users can send packages, groceries, or essentials within the city.
- Swiggy charges delivery fees for each hyperlocal service, creating a revenue stream beyond food delivery.
Swiggy’s expansion into Grocery and Essentials during the pandemic has added another revenue layer.
6. Cloud Kitchens: Swiggy Access
Swiggy has invested in cloud kitchens called Swiggy Access:
- These kitchens are virtual restaurants hosted by Swiggy partners.
- Restaurants can operate without physical dine-in spaces, reducing costs.
- Swiggy earns revenue through renting kitchen spaces, commissions, and increased order volume.
Cloud kitchens also increase restaurant reach in high-demand areas, benefiting Swiggy, restaurants, and customers alike.
Customer Segments
Swiggy serves three primary customer segments:
- Individual Consumers – People ordering food online for convenience.
- Restaurants – Businesses that want to increase sales and reach more customers.
- Delivery Partners – Freelance or part-time workers who earn income delivering orders.
By catering to multiple segments, Swiggy ensures consistent usage and network growth, similar to ride-hailing platforms like Ola or Uber.
Value Proposition
Swiggy’s value proposition is clear and resonates with all stakeholders:
- For Customers: Fast delivery, multiple cuisines, easy payment options, real-time tracking, and exclusive deals.
- For Restaurants: Access to a wide customer base, technology-driven order management, and marketing support.
- For Delivery Partners: Flexible work, income opportunities, and support infrastructure like fuel and maintenance assistance.
This triple-sided value proposition keeps all stakeholders engaged and loyal to the platform.
Key Resources
Swiggy relies on several key resources:
- Technology: App platform, AI-driven algorithms for order allocation, route optimization, and real-time tracking.
- Delivery Network: Thousands of delivery partners across cities, ensuring fast fulfillment.
- Brand and Marketing: Swiggy’s brand is recognized for speed, reliability, and convenience.
- Partnerships: Restaurants, cloud kitchen operators, payment gateways, and subscription services.
Without these resources, Swiggy wouldn’t be able to scale efficiently or maintain quality service.
Key Activities
Swiggy’s operations revolve around a few core activities:
- App Development and Maintenance: Ensuring smooth UI/UX, fast loading, and bug-free experience.
- Logistics Management: Efficiently connecting orders with nearby delivery partners.
- Customer Support: Handling complaints, refunds, and resolving order-related issues.
- Marketing and Promotions: Running ad campaigns, referral programs, and discounts.
- Partnership Management: Onboarding restaurants, cloud kitchens, and corporate tie-ups.
These activities are essential to maintain high service levels and user satisfaction.
Cost Structure
Running a platform like Swiggy is cost-intensive. Major costs include:
- Delivery Partner Incentives: Bonuses to encourage timely deliveries.
- Technology Costs: App maintenance, server infrastructure, AI algorithms, and R&D.
- Marketing Expenses: Discounts, referral rewards, campaigns, and brand promotions.
- Operational Costs: Salaries, support teams, and logistics management.
Swiggy invests heavily in customer acquisition and retention, which explains why profitability took time despite high revenue.
Swiggy’s Business Strategy
Swiggy’s growth strategy focuses on market penetration, diversification, and technology-driven efficiency.
1. Market Penetration
Swiggy initially focused on metros but expanded aggressively into Tier 2 and Tier 3 cities, where demand was rising but competition was lower. This helped the company capture a larger market share early on.
2. Diversification
Swiggy has diversified its offerings to include:
- Grocery and essentials delivery (Swiggy Instamart)
- Hyperlocal delivery services (Swiggy Genie)
- Cloud kitchens (Swiggy Access)
Diversification ensures Swiggy is not dependent solely on food delivery revenue.
3. Technology and AI
Swiggy invests heavily in AI and machine learning to:
- Optimize delivery routes
- Predict order demand
- Reduce delivery times
- Improve customer experience
4. Loyalty Programs
Swiggy Super encourages repeat usage by offering free deliveries, discounts, and exclusive deals. Loyal customers are more likely to order frequently, increasing overall revenue.
Challenges Swiggy Faces
Despite its success, Swiggy faces several challenges:
- Competition: Zomato, Dunzo, and local delivery services.
- High Operating Costs: Logistics, delivery partner incentives, and marketing expenses.
- Profitability Pressure: Heavy spending on discounts and acquisitions delays profitability.
- Regulatory Compliance: Food safety regulations, labor laws, and local restrictions can impact operations.
However, Swiggy continues to innovate and expand, which helps it stay ahead.
Key Metrics Driving Swiggy’s Success
Some of the metrics that matter for Swiggy include:
- Gross Merchandise Value (GMV): Total value of all orders on the platform.
- Active Users: Daily and monthly active customers.
- Order Frequency: Number of orders per user per month.
- Delivery Partner Retention: Number of active delivery partners over time.
- Market Share: Comparison with competitors in each city.
Monitoring these metrics allows Swiggy to improve operations, allocate incentives, and plan expansions effectively.
Swiggy vs Competitors
Swiggy competes mainly with Zomato, but also faces smaller players like Dunzo or local food delivery startups.
Differentiators for Swiggy:
- Hyperlocal focus: Efficient delivery in smaller towns and cities.
- Diversification: Swiggy Instamart, Genie, and cloud kitchens.
- Technology-driven logistics: AI algorithms optimize delivery speed and reduce costs.
- Customer Loyalty Programs: Swiggy Super ensures repeat usage.
These strategies help Swiggy maintain its lead in a competitive market.
Future Outlook
Swiggy is moving beyond food delivery to become a complete hyperlocal delivery platform. Future plans include:
- Expansion of grocery and essentials delivery
- Growth of cloud kitchens for new virtual brands
- Partnerships with FMCG companies for last-mile delivery
- Electric delivery vehicles to reduce operational costs and emissions
The focus is on diversifying revenue, reducing dependency on a single stream, and leveraging technology for scale.
Conclusion
Swiggy’s business model is simple yet sophisticated:
- Connect customers, restaurants, and delivery partners through a platform.
- Earn revenue from commissions, delivery fees, subscriptions, and advertising.
- Expand services to grocery, hyperlocal delivery, and cloud kitchens.
- Retain customers and delivery partners through loyalty programs and incentives.
Swiggy’s journey shows how technology, logistics, and customer-centric innovation can disrupt a traditional industry. It’s not just a food delivery app; it’s a complete hyperlocal logistics and tech platform.
For founders and entrepreneurs, Swiggy is a great example of how to build a multi-sided platform that scales efficiently while diversifying revenue streams.
Discover more from Business Model Hub
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.

Pingback: Zomato Business Model Explained: How Zomato Makes Money - Business Model Hub